Define the following terms from the language of hearing loss:
What will be an ideal response?
• Continuous noise - Noise of a constant level measured over at least one second using the "slow" setting on a sound level meter. Note that an intermittent noise (e.g., on for over a second and then off for a period) is both variable and continuous.
• Exchange rate - The relationship between intensity and dose. OSHA uses a 5-dB exchange rate. Thus, if the intensity of an exposure increases by 5 dB, the dose doubles. This may also be referred to as the doubling rate. The U.S. Navy uses a 4-dB exchange rate; the U.S. Army and U.S. Air Force use a 3-dB exchange rate.
• Hearing threshold level - The hearing level, above a reference value, at which a specified sound or tone is heard by an ear in a specified fraction of the trials. Hearing threshold levels have been established so that dB HTL reflects the best hearing of a group of persons.
• Noise-induced hearing loss - A sensorineural hearing loss that is attributed to noise and for which no other etiology can be determined.
• Time-weighted average - A value computed so that the resulting average is equivalent to an exposure resulting from a constant noise level over an eight-hour period.
You might also like to view...
A square with sides 5.3” long is cut from 16-gauge sheet metal. What is the square’s area, in square inches? Round the answer to the nearest tenth.
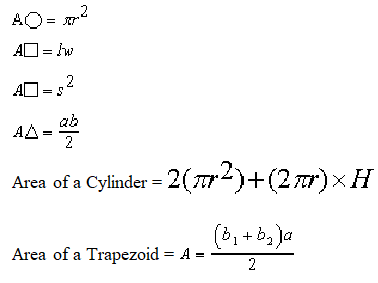
? Identify and state the historical significance of Victoria Woodhull.
What will be an ideal response?
Herbicides are often combined to give a product ____________________-spectrum weed control
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
A collision repair technician works on 147 cars per year, of which 17 percent require brake work. How many vehicles needing brake work are done each year? (Round to the nearest whole number.)
What will be an ideal response?