A portion (location) of DNA that encodes a specific protein is a
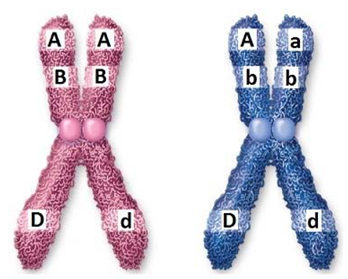
Examine this image of chromosomes and identify the structural components.
A. kinetochore.
B. centromere.
C. chromatid.
D. chromosome.
E. gene.
E. gene.
You might also like to view...
Based on what you know of ATP's chemistry, which of the following might be most likely to have possible similar uses in energy-management processes?
A. lysine (amino acid) B. phospholipids C. guanine nucleotide D. steroids E. potassium ions (K+)
In the 1860s, a Swiss chemist, Friedrick Miescher, isolated an acidic substance from cell nuclei. What was the name of this substance, and what was its significance?
What will be an ideal response?
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is important in maintaining homeostasis in mammals. ADH is released from the hypothalamus in response to high tissue osmolarity. In response to ADH, the collecting duct and distal tubule in the kidney become more permeable to water, which increases water reabsorption into the capillaries. The amount of hormone released is controlled by a negative feedback loop. Based on the model presented, which of the following statements expresses the proper relationship between osmolarity, ADH release, and urine production?
(A) As tissue osmolarity rises, more ADH is released, causing less water to be excreted as urine. (B) As tissue osmolarity rises, less ADH is released, causing less water to be excreted as urine. (C) As tissue osmolarity rises, more ADH is released, causing more water to be excreted as urine. (D) As tissue osmolarity rises, less ADH is released, causing more water to be excreted as urine.
The primary function of the mitochondrion is the production of ATP. To carry out this function, the mitochondrion must have all of the following except
A) the membrane-bound electron transport chain carrier molecules. B) proton pumps embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. C) enzymes for glycolysis. D) enzymes for the citric acid cycle. E) mitochondrial ATP synthase.