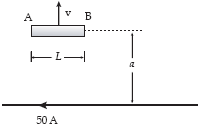
A conducting bar moves as shown near a long wire carrying a constant 50-A current. If a = 4.0 mm, L = 50 cm, and v = 12 m/s, what is the potential difference, VA ? VB?
a.
+15 mV
b.
?15 mV
c.
+20 mV
d.
?20 mV
e.
+10 mV
a
You might also like to view...
Unpolarized light passes through a combination of two ideal polarizers. The transmission axes of the first polarizer and the second polarizer are at 30.0° to each other. What percentage of the original light gets through the combination?
A) 37.5% B) 50% C) 75% D) 100%
A car needs to generate 75.0 hp in order to maintain a constant velocity of 27.3 m/s on a flat road. What is the magnitude of the total resistive force acting on the car (due to friction, air resistance, etc.)? (1 hp = 746 W)
A) 2.05 × 103 N B) 2.75 N C) 1.03 × 103 N D) 2.87 × 103 N
Wire A carries 4 A into a junction, wire B carries 5 A into the same junction, and another wire is connected to the junction. What is the current in this last wire?
A. 4 A away from the junction B. 9 A away from the junction C. 4 A into the junction D. 9 A into the junction E. 1 A away from the junction
Latent Heats: How much heat must be added to a 8.0-kg block of ice at -8°C to change it to water at 14°C? The specific heat of ice is 2050 J/kg ? C°, the specific heat of water is 4186 J/kg ? C°, the latent heat of fusion of ice is 334,000 J/kg, and 1 cal = 4.186 J.
A. 780 kcal B. 140 kcal C. 180 kcal D. 810 kcal E. 730 kcal