Use the dynamic aggregate demand and aggregate supply model and start with Year 1 in long-run macroeconomic equilibrium
For Year 2, graph aggregate demand, long-run aggregate supply, and short-run aggregate supply such that the condition of the economy will induce the Federal Reserve to conduct a contractionary monetary policy. Briefly explain the condition of the economy and what the Federal Reserve is attempting to do.
The Federal Reserve conducts a contractionary monetary policy to reduce inflation. In the graph below, the economy would move from point A in Year 1 to point B in Year 2 without any contractionary monetary policy. At point B, inflation is higher than it would be if real GDP equaled potential real GDP. The Fed would decrease the money supply and raise interest rates to slow down aggregate demand, trying to keep the economy at potential.
You might also like to view...
The rate of unemployment is found by
A) dividing the number unemployed by the number of people in the labor force. B) dividing the number employed by the number of people in the labor force. C) dividing the number unemployed by the number employed. D) dividing the number employed by the number unemployed.
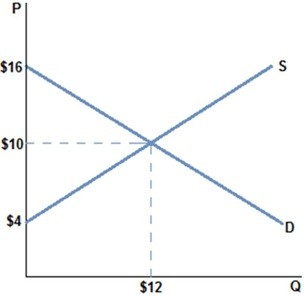 According to the graph shown:
According to the graph shown:
A. total surplus is smaller than producer surplus. B. total surplus is smaller than consumer surplus. C. producer surplus is greater than consumer surplus. D. consumer surplus is greater than producer surplus.
You're buying snacks for an Econ Club meeting. You've been given $100 to spend on chips and soda. If bags of chips cost $3 each and soda costs $1 each and you spend as much of your money as possible on chips, how many chips and sodas will you have for the meeting?
A. 33 bags of chips, 0 soda B. 33 bags of chips, 1 soda C. 34 bags of chips, 1 soda D. 34 bags of chips, 2 sodas
When income rises, total expenditures remain constant.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)