An emissions tax equal to the marginal social cost of pollution at ___________ induces those believed to be polluting to internalize the externality and leads to the socially optimal quantity of pollution.
a. the socially optimal quantity of pollution
b. the market-determined level of pollution
c. the market-determined level of production
d. zero pollution
Answer: a. the socially optimal quantity of pollution
You might also like to view...
Suppose a change in technology increases the marginal product of labor. The result is
a. a downward movement along the demand for labor curve. b. a rightward shift in the demand for labor curve. c. a leftward shift in the demand for labor curve. d. an upward movement along the demand for labor curve.
The pure monopolist who is nondiscriminating must decrease price on all units of a product sold in order to sell additional units. This explains why:
A. a monopoly has a perfectly elastic demand curve. B. there are barriers to entry in pure monopoly. C. marginal revenue is less than average revenue at all levels of output. D. total revenues are greater than total costs at the profit-maximizing level of output.
Accounting profit will always be
A) more than economic profit. B) equal to sunk costs. C) less than economic profit. D) equal to implicit costs.
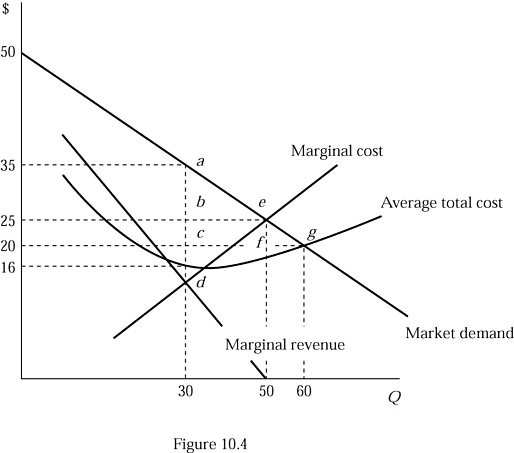 Refer to Figure 10.4. If the market was a monopoly, the consumer surplus would be:
Refer to Figure 10.4. If the market was a monopoly, the consumer surplus would be:
A. $625. B. $450. C. $300. D. $225.