Which of the following quantities is conserved for a planet orbiting a star in a circular orbit? Only the planet itself is to be taken as the system; the star is not included
a. Momentum and energy.
b. Energy and angular momentum.
c. Momentum and angular momentum.
d. Momentum, angular momentum and energy.
e. None of the above.
b
You might also like to view...
The motions of a car and a truck along a straight road are represented by the velocity-time graphs in the figure. The two vehicles are initially alongside each other at time t = 0. At time T, what is true about these two vehicles since time t = 0?
A) The truck will have traveled further than the car. B) The car will have traveled further than the truck. C) The truck and the car will have traveled the same distance. D) The car will be traveling faster than the truck.
As the moon covers the solar disk during a solar eclipse, a flash spectrum of the sun's chromosphere can be recorded. This flash spectrum reveals an emission spectrum and provides information on the properties of the chromosphere. As the moon moves from the inner chromosphere to the outer chromosphere, the spectral lines present in the flash spectrum change. What is going on in the chromosphere
that produces the changes in the flash spectrum? I. The temperature of the chromosphere decreases as the distance from the photosphere increases. II. The temperature of the chromosphere increases as the distance from the photosphere increases. III. The density of the chromosphere decreases as the distance from the photosphere increases. IV. The density of the chromosphere increases as the distance from the photosphere increases. a. I & III b. I & IV c. II & III d. II & IV e. I
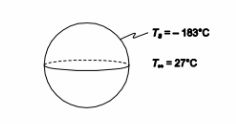
A cryogenic fluid is stored in a 0.3-m-diameter spherical container in still air. If the convection heat transfer coefficient between the outer surface of the container and the air is 6.8 W/(m2 K), the temperature of the air is 27°C and the temperature of the surface of the sphere is –183°C, determine the rate of heat transfer by convection.
GIVEN
• A sphere in still air
• Sphere diameter (D) = 0.3 m
• Convective heat transfer coefficient ch = 6.8 W/(m2K)
• Sphere surface temperature (Ts) = –183°C
• Ambient air temperature (T?) = 27°C
FIND
• Rate of heat transfer by convection (qc)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state heat flow
SKETCH
An amount of work equal to 2.0 J is required to compress the spring in a spring-gun. What is the "launch speed" of a 26.0-g marble?
a. 12.4 m/s b. 13.4 m/s c. 8.8 m/s d. 3.92 m/s e. 0.392 m/s