If a central bank were required to target inflation at zero, then when there was an unanticipated increase in aggregate supply the central bank
a. would have to increase the money supply. This would move unemployment closer to the natural rate.
b. would have to increase the money supply. This would move unemployment further from the natural rate.
c. would have to decrease the money supply. This would move unemployment closer to the natural rate.
d. would have to decrease the money supply. This would move unemployment further from the natural rate.
b
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. A borrower sells bonds, and a lender buys bonds. 2. A change in the price of bonds causes a change in interest rates. 3. A bond that promises a series of payments on different dates is a perpetuity. 4. It would be irrational to promise to make an infinite number of payments in exchange for a finite amount of goods. 5. The present value of a perpetuity falls when the interest rate rises.
Firms may experience diseconomies of scale when
a. they are too small to take advantage of specialization. b. large management structures are bureaucratic and inefficient. c. there are too few employees, and managers do not have enough to do. d. average fixed costs begin to rise again.
Figure 2-2

Assume that U.S. agricultural land is used either to raise cattle for beef or to grow wheat. represents the production possibility frontier for beef and wheat. Between points F and G, the opportunity cost increasing wheat by two bushels equals
a.
0.25 million pounds of beef
b.
1.75 million pounds of beef
c.
0.125 pounds of beef
d.
8.0 pounds of beef
e.
0.5 pounds of beef
Exhibit 14-8 Aggregate demand and supply
?
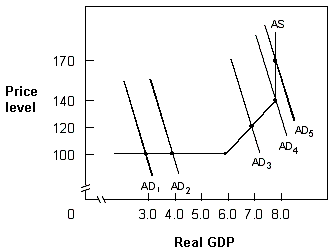
A. cost-push inflation. B. cost-pull inflation. C. demand-push inflation. D. demand-pull inflation.