A 3.0-kg mass moving in the positive x direction with a speed of 10 m/s collides with a 6.0-kg mass initially at rest. After the collision, the speed of the 3.0-kg mass is 8.0 m/s, and its velocity vector makes an angle of 35° with the positive x axis. What is the magnitude of the velocity of the 6.0-kg mass after the collision?
a. 2.2 m/s
b. 2.9 m/s
c. 4.2 m/s
d. 3.5 m/s
e. 4.7 m/s
B
You might also like to view...
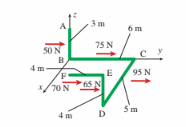
On bracket ABCDEF, each y-direction force acts at the center of the bar segment to which it is applied (see figure). All turns of ABCDEF are 90o angles. The resultant moment at B (MB) for this parallel force system is (in N?m)
(A) 395j 1 1080k
(B) 415i 1 875k
(C) 485i 2 913k
(D) 2485i 1 913k
An electron in the hydrogen atom has a wavelength of 2.67 nm. To what state of the hydrogen atom does this electron belong?
A) n = 2 B) n = 5 C) n = 8 D) n = 11 E) n = 14
A 5.00 kg mass is located at (1.0 m, 0.00 m, 3.00 m), a 2.00 kg mass is located at (0.00 m, 3.00 m, – 2.00 m), and a 3.00 kg mass is located at (–1.0 m, –2.00 m , 0.00 m). The center of gravity of the system of masses is
A. (1/10m, 10/10m, 1/10m). B. (2/10m, 0m, 11/10m). C. (3/10m, 2/10m, 10/10m). D. (10/10m, 2/10m, 3/10m). E. (2/10m, 10/10m, 0m).
Two cars collide head-on on a level friction-free road. The collision was completely inelastic and both cars quickly came to rest during the collision. What is true about the velocity of this system's center of mass?
A) It was always zero. B) It was never zero. C) It was not zero, but ended up zero. D) none of the above