The potential for a financial breakdown at large institutions to spread throughout the financial system is called
A) a systemic risk.
B) a too-large-to-fail problem.
C) an averse selection problem.
D) a moral hazard.
A
You might also like to view...
The Who-Needs-A-Doctor? Company makes a do-it-yourself rhinoplasty kit. The company is deciding whether to include a safety feature that would cost $40 for each kit
The company estimates the probability of death without the safety feature is 1/10,000 and the death cost per kit is $50. Based on this information, answer the following questions: a. What is the value the company has placed on a life? b. What is the company's cost-benefit recommendation? c. If the company has overestimated the probability of death and the true probability of death is 1/15,000, what is the true death cost per rhinoplasty kit? d. If the company has overestimated the probability of death and the true probability of death is 1/15,000, what would the true cost-benefit recommendation be for the company? e. If the company has correctly estimated the probability of death but has underestimated by one-half the true value of a life, what is the true death cost per rhinoplasty kit? f. If the company has correctly estimated the probability of death but has underestimated by one-half the true value of a life, what would the true cost-benefit recommendation be for the company?
Suppose all tickets to the World Series have already been sold. Will any further sales occur if the going price rises?
A) No, and therefore a higher price will have no effect. B) No, but a smaller quantity will be demanded. C) Not unless more tickets are printed. D) Yes, as some ticket-holders sell to others. E) Yes, but the further sales will reduce the price to the original level.
Under what condition will a decrease in aggregate demand result in no decline in the price level?
A. The aggregate demand curve intersects an upward-sloping segment of the aggregate supply curve. B. The aggregate demand curve intersects a vertical segment of the aggregate supply curve. C. The aggregate demand curve is upward sloping. D. The aggregate demand curve intersects a horizontal segment of the aggregate supply curve.
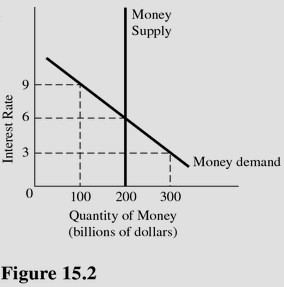 In Figure 15.2, at an interest rate of 9 percent, there is
In Figure 15.2, at an interest rate of 9 percent, there is
A. An excess supply of money of $100 billion. B. An excess supply of money of $200 billion. C. Equilibrium in the money market. D. An excess demand for money of $100 billion.