A larger crowding-out effect:
a. increases the magnitude of a given fiscal policy's effect on interest rates and increases the magnitude of its effects on investment.
b. increases the magnitude of a given fiscal policy's effect on interest rates and decreases the magnitude of its effects on investment.
c. decreases the magnitude of a given fiscal policy's effect on interest rates and increases the magnitude of its effects on investment.
d. decreases the magnitude of a given fiscal policy's effect on interest rates and decreases the magnitude of its effects on investment.
a
You might also like to view...
When government pays individuals to purchase pollution-reducing devices, that payment is called a subsidy
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The production of steel in a factory generates a negative externality. A per-unit tax on the factory that equals ________ of steel production will internalize the externality entirely
A) the marginal private cost B) the marginal social cost C) the marginal external cost D) the marginal external benefit
If you want to vote for the management of the corporation, you should buy
A) common stock. B) preferred stock. C) bonds. D) either common stock or preferred stock.
Figure 14-5
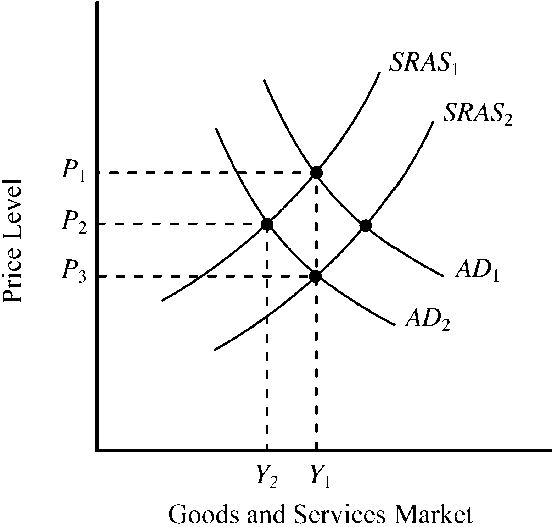
In , AD1 and SRAS1 indicate an economy initially operating at full-employment output level, Y1. The long-run impact of the Fed unexpectedly shifting to a more restrictive monetary policy will be
a.
a decrease in aggregate demand to AD2 and a decrease in real output to Y2.
b.
a decrease in the full-employment level of output to Y2.
c.
a decrease in aggregate demand to AD2 and an increase in short-run aggregate supply to SRAS2, causing the price level to fall to P3 and real output to remain unchanged at Y1.
d.
no change; AD and SRAS will stay at AD1 and SRAS1.