Use the IS-LM model to determine the effects of each of the following on the general equilibrium values of the real wage, employment, output, the real interest rate, consumption, investment, and the price level.(a)Tougher immigration laws reduce the working-age population.(b)There's increased volatility in the prices of stocks and bonds.(c)The government tries to achieve tax equity by an increase in the corporate tax rate.(d)Increased computerization reduces stock market brokerage costs.
What will be an ideal response?
| (a) | The decline in labor supply increases the real wage and reduces employment and output, |
| (b) | Real money demand rises, which shifts the LM curve up and to the left. To restore equilibrium, |
| (c) | The higher tax rate reduces investment, shifting the IS curve down and to the left. To restore |
| (d) | Increased liquidity on nonmoney assets reduces money demand, shifting the LM curve down |
You might also like to view...
Checking deposits at banks are
A) money. B) not money because they are an intangible. C) money only because they are insured by the FDIC. D) not money until they are converted into currency.
If the price of a pizza increases and the demand curve for pizza does not shift, then the consumer surplus from pizza will ________
A) increase B) decrease C) equal the producer surplus if the market produces the efficient quantity of pizza D) remain the same
If a road is congested, then use of that road by an additional person would lead to a
a. negative externality. b. positive externality. c. Pigovian externality. d. free-rider problem with rush hour drivers stuck in traffic.
To answer the question, refer to the following table showing a demand schedule: 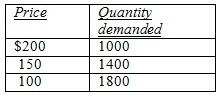 If price falls from $150 to $100,
If price falls from $150 to $100,
A. an arrow representing the price effect points down and is shorter than an arrow for the quantity effect. B. arrows representing the price and quantity effects both point down. C. total revenue moves in the same direction as the arrow representing the price effect. D. the arrow representing the price effect points down and the arrow representing the quantity effect points up. E. both c and d