Because private owners are held responsible for damages their property causes to the property of others, private owners have
a. a strong incentive to take steps to reduce the chance that they will harm the property of others.
b. a strong incentive to use their property now rather than conserving it for the future.
c. little incentive to take good care of the property.
d. little incentive to consider the harm their property may do to the property of others.
A
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements is correct?
a. The classical aggregate AD curve can be shifted by monetary and non-monetary factors. b. The classical AS schedule is horizontal while the Keynesian aggregate AS schedule is vertical. c. The Keynesian AD curve only shifts in response to monetary factors. d. The classical aggregate supply schedule slopes upward to the right while the Keynesian aggregate supply schedule is vertical. e. none of the above are correct.
When people anticipate a company’s earnings will drop, prospective stockholders want to pay ______ for a stock, and current stockholders ______ to sell.
a. less; are eager b. more; are eager c. less; are reluctant d. more; are reluctant
The production possibilities curve shows that:
a. some of one good must be given up to get more of another good in an economy that is operating efficiently.
b. no output combination is impossible.
c. an economy that is operating efficiently can have more of one good without giving up some of another good.
d. scarcity can be eliminated.
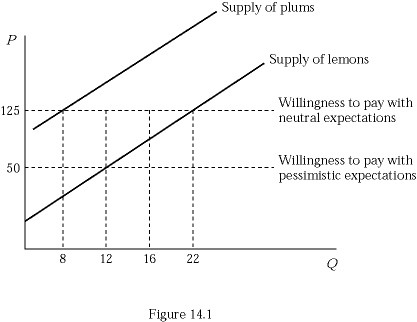 Figure 14.1 represents the market for used bikes. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $200 for a plum (high-quality) used bike and $50 for a lemon (low-quality) used bike. Initially buyers believe that 50% of used bikes in the market are lemons (low quality). Compared to the outcome with neutral expectations, how many fewer bikes are sold in equilibrium?
Figure 14.1 represents the market for used bikes. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $200 for a plum (high-quality) used bike and $50 for a lemon (low-quality) used bike. Initially buyers believe that 50% of used bikes in the market are lemons (low quality). Compared to the outcome with neutral expectations, how many fewer bikes are sold in equilibrium?
A. 8 B. 12 C. 18 D. 22