If opportunity costs are constant, then
A) the production possibilities curve does not exist.
B) the production possibilities curve bows outward.
C) the production possibilities curve is a negatively sloped straight line.
D) factors of production must not be fully employed.
C
You might also like to view...
A consequence of a negative externality is that social costs __________ private costs, and the efficient level of output __________.
A. equal; does not require any type of government intervention B. are less than; requires the government to create a subsidy C. are greater than; requires the government to impose a tax D. are greater than; requires the government to create a subsidy E. are less than; requires the government to impose a tax
Assume that the central bank increases the reserve requirement. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the quantity of real loanable funds per time period and reserve-related (central bank) transactions in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period rises, and reserve-related (central bank) transactions becomes more positive (or less negative). b. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period rises, and reserve-related (central bank) transactions remain the same. c. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables. d. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period falls, and reserve-related (central bank) transactions remain the same. e. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period and reserve-related (central bank) transactions remain the same.
Figure 3-16
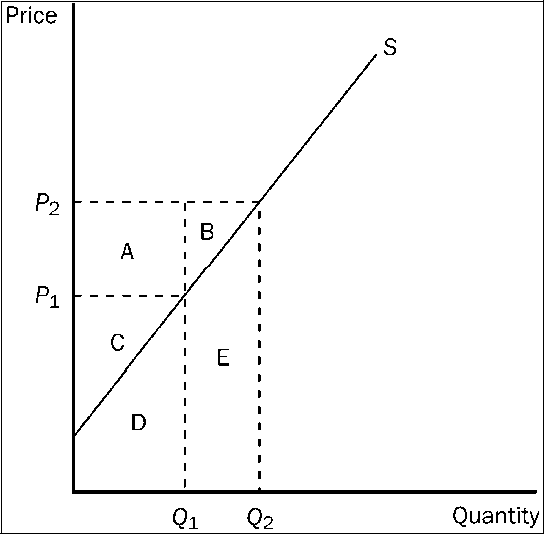
Refer to . When the price is P1, producer surplus is
a.
A.
b.
C.
c.
A + B.
d.
C + D.
A change in which of the following will have a direct effect on the amount of money individuals wish to hold in the current period?
A) the current nominal interest rate B) the current real interest rate C) the expected future nominal interest rate D) the expected future real interest rate E) all of the above