Everything else equal, a depreciation of the dollar will:
A) cause the GDP of the U.S. to fall. B) cause the inflation rate in the U.S. to decrease.
C) cause the GDP of the U.S. to increase. D) cause the net exports of the U.S. to decrease.
C
You might also like to view...
Player 1 and Player 2 are playing a game in which Player 1 has the first move at A in the decision tree shown below. Once Player 1 has chosen either Up or Down, Player 2, who can see what Player 1 has chosen, must choose Up or Down at B or C. Both players know the payoffs at the end of each branch. 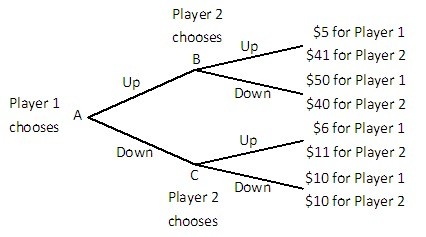 If Player 2 could make a credible commitment to choose either Up or Down when his or her turn came, then what would Player 2 do?
If Player 2 could make a credible commitment to choose either Up or Down when his or her turn came, then what would Player 2 do?
A. Player 2 would commit to choosing Down. B. Player 2 would commit to choosing Up. C. Player 2 would not commit to choosing either strategy. D. Player 2 would commit to mimicking Player 1's strategy.
Assuming all else equal, if there is a contraction in the quantity of bank account balances, it will cause:
A) a downward movement along the demand curve for reserves. B) a leftward shift in the demand curve for reserves. C) a rightward shift in the demand curve for reserves. D) an upward movement along the demand curve for reserves.
A dirty float is an example of ________
A) a fixed exchange rate system B) a flexible exchange rate system C) a revaluation D) a currency board
Suppose Happy Cows has a marginal cost equal to 0.5Q and Free Cows has a marginal cost equal to 2Q.
A) All else equal, neither Free Cows nor Happy Cows can benefit from an accurate forecast. B) All else equal, an accurate forecast is more valuable to Free Cows than Happy Cows. C) All else equal, an accurate forecast has the same value to both Free Cows and Happy Cows. D) All else equal, an accurate forecast is more valuable to Happy Cows than Free Cows.