Refer to Figure 12-5. The firm's manager suggests that the firm's goal should be to maximize average profit. In that case, what is the output level and what is the average profit that will achieve the manager's goal?
A) Q = 1,800 units, average profit = $20 B) Q = 1,350 units, average profit = $5
C) Q = 1,100 units, average profit = $6 D) Q = 1,350 units, average profit = $9
C
You might also like to view...
Advertising by firms in monopolistic competition
A) provides consumers with no useful information. B) does not occur. C) can persuade customers that product differentiation exists. D) wastes resources because the entry of rivals forces firms to be price takers.
Darryl graduated with honors from college. However, he obtained his outstanding grades by cheating on every final exam with help from his best friend; Darryl actually has the talent of a C student. Nevertheless, he gets a job with a top accounting firm in Boston. The fact that he is hired illustrates a failure of
a. comparable worth b. signaling and screening c. marginal productivity d. supply and demand e. specialization
The minimum efficient scale of a firm:
A. is the smallest level of output at which long-run average total cost is minimized. B. is in the middle of the range of constant returns to scale. C. occurs where marginal product becomes zero. D. is realized somewhere in the range of diseconomies of scale.
Below, the graph on the left shows long-run average and marginal cost for a typical firm in a perfectly competitive industry. The graph on the right shows demand and long-run supply for an increasing-cost industry.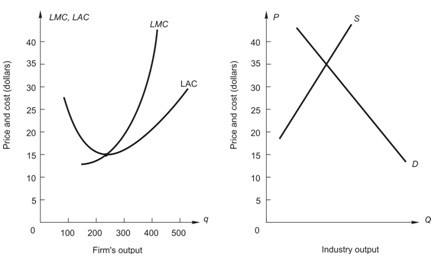 If this were an increasing cost industry, what would be the price when the industry gets to long-run competitive equilibrium?
If this were an increasing cost industry, what would be the price when the industry gets to long-run competitive equilibrium?
A. $35 B. between $35 and $15 C. below $15 D. above $35 E. $15