Which molecule moves with the fastest average speed while being bound in Earth's atmosphere in thermal equilibrium?
a. Water, H2O (atomic mass = 18)
b. Carbon dioxide, CO2 (atomic mass = 44)
c. Nitrogen (atomic mass = 28)
d. Oxygen (atomic mass = 32)
e. Hydrogen, H2 (atomic mass = 2)
e. Hydrogen, H2 (atomic mass = 2)
You might also like to view...
The eyepiece of a compound microscope has a focal length of 2.50 cm and the objective has a focal length of 1.60 cm. The two lenses are separated by 15.0 cm. The microscope is used by a person with normal eyes (near point at 25 cm)
What is the angular magnification of the microscope? A) 195 x B) 125 x C) 94 x D) 234 x E) 78 x
A diatomic molecule has 2.6 × 10-5 eV of rotational energy in the L = 2 quantum state. What is the rotational energy in the L = 1 quantum state?
A) 3.4 × 10-6 eV B) 4.1 × 10-6 eV C) 5.3 × 10-6 eV D) 7.8 × 10-6 eV E) 8.7 × 10-6 eV
Addition by 1. Components: Three forces, 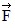 1,
1, 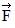 2, and
2, and 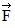 3, all act on an object, as shown in the figure. The magnitudes of the forces are: F1 = 80.0 N, F2 = 60.0 N, and F3 = 40.0 N. The resultant force acting on the object is given by
3, all act on an object, as shown in the figure. The magnitudes of the forces are: F1 = 80.0 N, F2 = 60.0 N, and F3 = 40.0 N. The resultant force acting on the object is given by 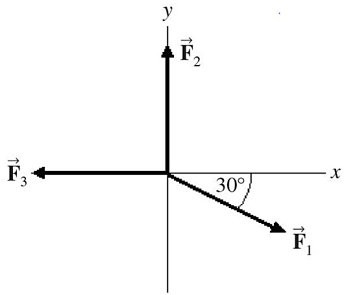
A. 180 N at an angle of 60.0° with respect to +x-axis. B. 60.0 N at an angle of 90.0° with respect to +x-axis. C. 20.0 N at an angle of 34.3° with respect to +x-axis. D. 35.5 N at an angle of 34.3° with respect to +x-axis. E. 40.0 N at an angle of 60.0° with respect to +x-axis.
What are the two largest moons of Neptune and what makes them peculiar objects in our Solar System?
What will be an ideal response?