The banding patterns are different for non-homologous chromosomes. Indicate whether the statement is true or false
T
You might also like to view...
In the graph below, how can the change in infant mortality be explained as birth weight increases from 2 to 7 pounds?
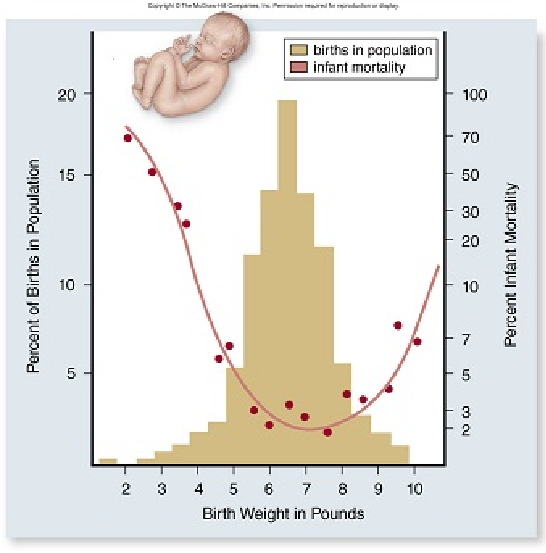
A. A larger baby will have more developed organs and thus have greater fitness.
B. A baby closer to 7 pounds will have more developed organs and thus have lower mortality.
C. A baby closer to 2 pounds will not be able to be delivered safely and thus have lower mortality.
D. A baby closer to 7 pounds will have more developed organs and thus have higher motality.
E. A baby closer to 7 pounds will not be able to be delivered safely and thus have higher mortality.
Clarify Question
· What is the key concept addressed by the question?
· What type of thinking is required?
· What key words does the question contain and what do they mean?
Gather Content
· What do you already know about fitness? How does it relate to the question?
Consider Possibilities
· What other information is related to the question? Which information is most useful?
Choose Answer
· Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflect on Process
· Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
As you are reading this question, your brain interprets the information and a __________ is
required for you to physically circle the correct answer.
a. CNS b. sensory input c. motor output d. pheromone
sea microbes
What will be an ideal response?
During anaerobic respiration, a compound can serve as an electron donor as long as the ________ of the redox couple is ________ electronegative than that of the acceptor couple
a. E0´ / less b. E0´ / more c. ?G0´ / less d. ?G0´ / more