In the Bertrand model,
A. each firm takes the quantities produced by its rivals as given.
B. one firm plays a leadership role and its rivals merely follow.
C. each firm takes the prices charged by its rivals as given.
D. prices are higher and quantities are slightly less than we would see if the firms colluded to achieve the monopoly outcome.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
In the long-run equilibrium of a monopolistically competitive industry
A. P = MC. B. P > minimum (ATC). C. P < MC. D. P = minimum (ATC).
In an oligopoly price-fixing game, each player tries to
A) minimize the market shares of its opponents. B) maximize its own market share. C) minimize the profits of its opponents. D) maximize its own profit.
Refer to the table below for a prisoner’s dilemma. Frank and George are arrested and charged with armed robbery. They are isolated in separate interrogation rooms and therefore are not allowed to engage in collusion to collectively deny committing the crime. The table shows the four possible outcomes for denial and confession for Frank and George. The payoff to Frank is in the upper corner of each box, and the payoff to George is in the lower corner of each box. The most likely outcome is
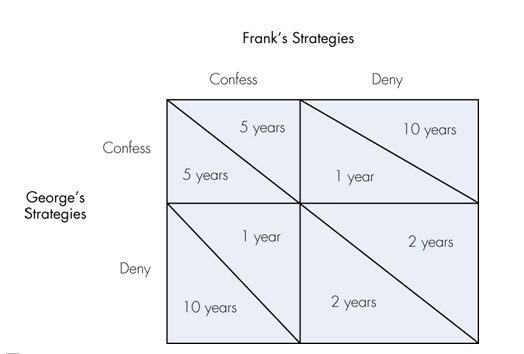
a. for both to confess and spend 5 years in prison.
b. for both to deny and spend 2 years in prison.
c. for George to deny and spend 10 years in prison and Frank to confess and spend 1 year in prison.
d. for George to confess and spend 1 year in prison and Frank to deny and spend 10 years in prison.
Government economic policies are designed to have the biggest impact on _____
a. cyclical unemployment b. frictional unemployment c. structural unemployment d. seasonal unemployment