The table above gives the demand schedule for museum visits
a. You, as the resident economist, have been given the task of maximizing the museum's total revenue. What admission price should you charge?
b. What is the elasticity of demand between $6 and $4?
c. Moving along the demand schedule from $10 to $8 to $6 and ultimately to $4, how does the price elasticity of demand change in size?
a. The admission price you should charge is $6. The total number of visits will be 300,000 and total revenue is $6 × 300,000 = $1,800,000. No other price gives you this much total revenue.
b. The price elasticity of demand equals [(300 visits - 400 visits) ÷ 350 visits] ÷ [($6 - $4 ) ÷ $5] =
(0.29 ) ÷ (0.4 ) = 0.71.
c. Moving along the demand schedule to lower prices, the elasticity of demand falls in size.
You might also like to view...
To achieve long-run equilibrium in an economy with a recessionary gap, without the use of stabilization policy, the inflation rate must:
A. not change. B. increase. C. decrease. D. either increase or decrease depending on the relative shifts of AD and AS.
Which of the following terms best describes the situation in which a country is running both a trade and a budget deficit?
a. neutral deficits b. twin deficits c. Ricardian equivalence d. balance of trade
Which of the following is not used in the stage of external search?
Friends and family members Government sources The Internet All can be used
This problem should be done in four steps. First, fill in the table directly below. Assume that fixed cost is $100 and price is $79. Second, on the graph paper draw the graphs of the firm's demand, marginal revenue, average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost curves. Be sure you label the graph correctly. Indicate the firm's short-run and long-run supply curves, and the break-even and shutdown points. Third, calculate total profit in the space below and then answer questions A-D. Fourth, complete the second table.
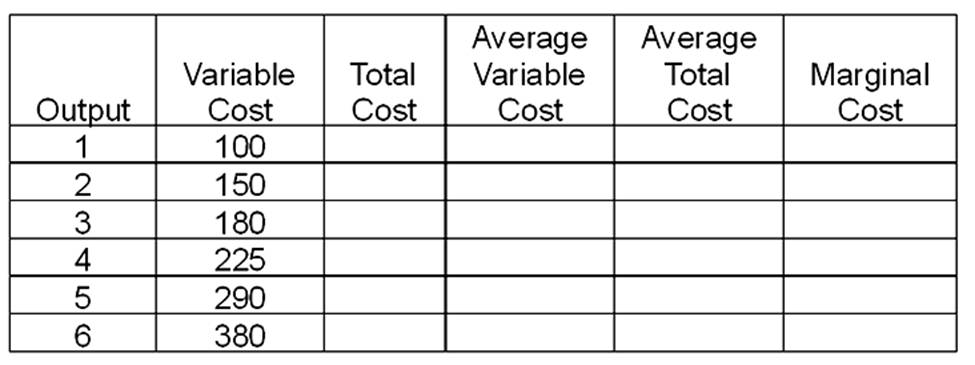
A. The minimum price the firm would accept in the short run would be $___________.
B. The minimum price the firm would accept in the long run would be $___________.
C. The output at which the firm would operate most efficiently would be ___________.
D. The output at which the firm would maximize profits would be ___________.
