A preferred stock is expected to pay a $0.75 dividend every quarter indefinitely. If the required rate of return is 10% with quarterly compounding, what formula in B3 can be used to determine the value of this stock?
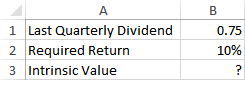
a) =B1/B2/4
b) =B1/B2
c) =B1/(B2/4)
d) =B1*4/(B2/4)
e) =B1/(B3/4)
c) =B1/(B2/4)
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. Role overload is a state of emotional, mental, and physical exhaustion, expressed as listlessness, indifference, or frustration. 2. Extra staff at peak periods is an example of buffers managers can use to prevent employee burnout. 3. Employee assistance programs focus on self-responsibility, nutritional and environmental awareness, relaxation techniques, and physical fitness. 4. In managing for motivation, you should think about employees as capital assets.
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. Programmed decisions respond to new or nonroutine problems for which there are no proven solutions. 2. Usually programmed decisions relate to situations that have occurred in the past and are familiar to the people dealing with them. 3. The last step of the five-step model of decision-making is to rate alternatives on the basis of decision criteria. 4. There are five steps to the decision-making model explained in the textbook, including generate and evaluate alternatives.
In which of the following situations is the individual not actively engaged in selling?
A. Brendan is persuading Meryl to loan him $10 so he can order a pizza. B. Chad is trying to convince his biology lab partner to sketch the internal organs of the frog they dissected in lab. C. Daniel is creating a logo for his home-based Web services company. D. Steve is trying to convince his professor that he deserves an "A." E. Anna is trying to persuade her husband to attend her family reunion.
U.S. GAAP requires firms holding securities available-for-sale to value the securities on the balance sheet after acquisition at
a. an amount based on acquisition cost. b. market value, with changes in market value of securities held at the end of the accounting period reported each period in income. c. market value, with changes in market value of securities held at the end of the accounting period not affecting reported income until the firm sells, or otherwise disposes of, the securities. d. market value, with changes in market value of securities held at the end of the accounting period reported each period in retained earnings. e. present value of future cash flows, with changes in market value of securities held at the end of the accounting period reported each period in retained earnings.