Normal profit is defined as a(n):
a. foregone percent rate of return.
b. opportunity profit.
c. implicit profit.
d. minimum necessary to keep a firm in operation.
d
You might also like to view...
Which of the following outcomes is NOT a result of a tax imposed on sellers of gasoline?
A) Supply decreases, a deadweight loss is created, and the price rises. B) The market becomes less efficient and the government collects the tax revenue. C) Demand does not change, the price rises, and consumer surplus decreases. D) Demand decreases, the market becomes more efficient, and the price rises.
The excludability versus nonexcludability issue is
A. relevant to the issue of market failure. B. not relevant to the issue of market failure. C. relevant to the free-rider problem. D. a and c E. b and c
Economist A believes the economy is self-regulating. Economist B believes that wages and prices are inflexible downward. Economist C believes that the AS curve is vertical. Economist D believes that crowding out is likely to be complete. Which economist is most likely to advocate for expansionary fiscal policy in the in the form of greater government spending to remove an economy from a
recessionary gap? A) Economist A B) Economist B C) Economist C D) Economist D
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.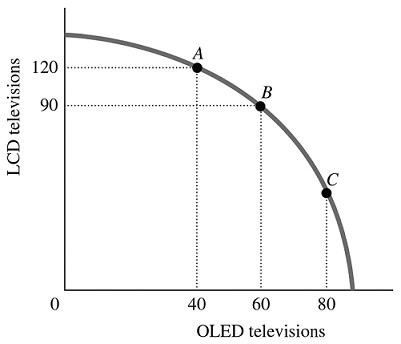 Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point A. The opportunity cost of moving from Point A to Point B is the
Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point A. The opportunity cost of moving from Point A to Point B is the
A. 30 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 60 additional OLED televisions. B. 90 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 20 additional OLED televisions. C. 30 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 20 additional OLED televisions. D. 120 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 40 additional OLED televisions.