The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA does not produce any ATP directly. However, it does contribute to ATP production indirectly. How?
What will be an ideal response?
Answers will vary
You might also like to view...
Which one of the following types of fatty acids would be likely to have the lowest melting temperature?
A. long tails and low saturation B. long tails and high saturation C. short tails and low saturation D. short tails and high saturation E. All fatty acids have the same melting temperature regardless of tail length or level of saturation.
The age of a fossil can be estimated by analyzing the decay of radioisotopes within the accompanying rock. If you suspected a fossil was 100 million years old, which type of radioisotopes would you use to analyze the accompanying rock?
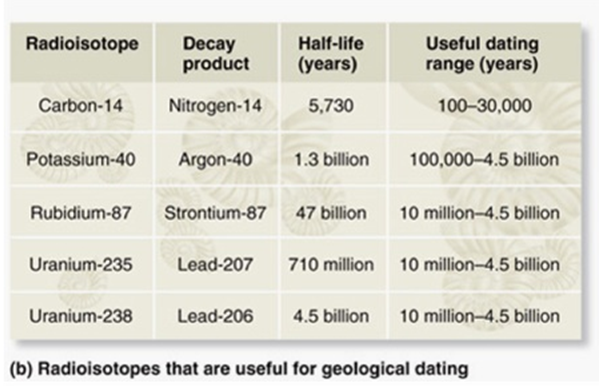
A. Potassium-40/Argon-40 (half-life = 1.3 billion years; useful dating range =100,000-4.5 billion years)
B. Rubidium-87/Strontium-87 (half-life = 47 billion years; useful dating range = 10 million-4.5 billion years)
C. Uranium-235/Lead-207 (half-life = 710 million years; useful dating range = 10 million-4.5 billion years)
D. Carbon-14/Nitrogen-14 (half-life = 5,730 years; useful dating range = 100-50,000 years)
E. Uranium-238/Lead-238 (half-life 4.5 billion years; useful dating range = 10 million-4.5 billion years)
Under which weather condition would transpiration be most rapid?
A) hot, humid weather B) cold, humid weather C) hot, dry weather D) windy, wet weather
Which of the following statements is true of selective toxicity?
A. Selective toxicity takes advantage of structural similarities between host and pathogen. B. To be effective, an antimicrobial agent must be more toxic to the patient than the pathogen. C. Selective toxicity takes advantage of differences in metabolic rates of the host and pathogen. D. Selective toxicity damages only pathogenic bacteria and not beneficial bacteria. E. Selective toxicity takes advantage of structural and/or metabolic differences between host and pathogen.