A baseball catcher throws a ball vertically upward and catches it in the same spot when it returns to his mitt. At what point in the ball's path does it experience zero velocity and non-zero acceleration at the same time?
a. midway on the way up
b. at the top of its trajectory
c. the instant it leaves the catcher's hand
d. the instant before it arrives in the catcher's mitt
b
You might also like to view...
The top panorama shows our view of the Milky Way in all directions as it appears in visible light. The bottom panorama shows the same view, but in a different wavelength of light. What wavelength band are we seeing in the bottom photo, and how do you know?
A) infrared light, because the dust that appears dark in the visible light photo glows in infrared light B) x-ray light, because only x-rays allow us to see through the disk of our galaxy C) radio waves, because clouds of gas in the disk of our galaxy appear pinkish when we look at them with radio telescopes D) infrared light, because clouds of gas and dust appear pinkish when we look at them with infrared telescopes
You obtain a 100-W light bulb and a 50-W light bulb. Instead of connecting them in the normal way, you devise a circuit that places them in series across normal household voltage
If each one is an incandescent bulb of fixed resistance, which statement about these bulbs is correct? A) Both bulbs glow with the same brightness, but less than their normal brightness. B) Both bulbs glow with the same brightness, but more than their normal brightness. C) The 100-W bulb glows brighter than the 50-W bulb. D) The 50-W bulb glows more brightly than the 100-W bulb.
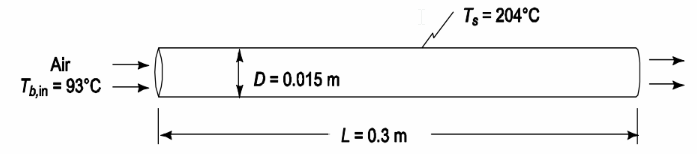
Suppose an engineer suggests that air instead of water could flow through the tube and the velocity of the air could be increased until the heat transfer coefficient with the air equals that obtained with water at 1.5 m/s. Determine the velocity required and comment on the feasibility of the engineer’s suggestion. Note that the speed of sound in air at 100°C is 387 m/s.
GIVEN
• Air flow through a tube
• Bulk inlet air temperature (Tb,in) = 93°C
• Tube diameter (D) = 0.015 m
• Tube length (L) = 0.3 m
• Tube surface temperature (Ts) = 204°C
• From Problem 7.32: h ,c L = 13,037 W/(m2 K)
FIND
• The velocity (V) required to obtain h ,c L = 13,037 W/(m2 K)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• Constant and uniform tube temperature
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the inlet bulk temperature of 93°C
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0302 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 22.9 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
A circular conducting loop lies in the xy plane of a certain reference frame. We are looking down on the loop with the +z axis pointing up at us. If the loop is immersed in a magnetic field that points in the -z direction and is increasing in magnitude as time passes, which way will current flow in the loop?
A. Counterclockwise B. Clockwise C. No current will flow.