You push on a block on frictionless ice with a force of 8 N, causing it to accelerate at 2 m/s2 . The mass of the block is
a. 2 kg.
b. 4 kg.
c. 8 kg.
d. 16 kg.
e. 6 kg.
b
You might also like to view...
A cylinder containing an ideal gas has a volume of 3.0 m3 and a pressure of 1.0 × 10^5 Pa at a temperature of 300 K. The cylinder is placed against a metal block that is maintained at 900 K, and the gas expands as the pressure remains constant until the temperature of the gas reaches 900 K. The change in internal energy of the gas is +6.0 × 10^5 J. How much heat did the gas absorb?
a. 0 c. 12 × 10^5 J b. 6.0 × 10^5 J d. 9.0 × 10^5 J
What is the principle of isostasy, and what evidence supports it?
What will be an ideal response?
What is the potential difference VB ? VA when I = 0.50 A in the circuit segment shown below?
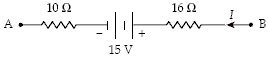
a.
+28 V
b.
+2.0 V
c.
?28 V
d.
?2.0 V
e.
+18 V
Energy Conservation With Nonconservative Forces: On a planet where g = 10.0 m/s2 and air resistance is negligible, a sled is at rest on a rough inclined hill rising at 30° as shown in the figure. The object is allowed to move and it stops on a rough horizontal surface, at a distance of 4.0 m from the bottom of the hill. The coefficient of kinetic friction on the hill is 0.40. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the horizontal surface and the sled?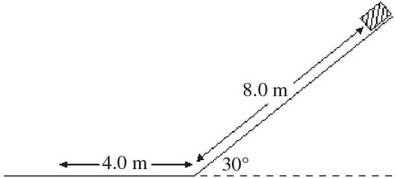
A. 0.10 B. 0.20 C. 0.31 D. 0.40 E. 0.60