Fashion Buyers I A buyer for a department store must decide on which designs the stores will carry before he knows what the demand will be in the coming season. Choosing a poorly demanded design means lots of unsold merchandise and losses that are
$200,000 on average. Passing on a highly demanded design means unsold merchandise and missing out on profits that are $300,000 on average. What probability of a design's success should he be in order to choose to carry it?
Under the hypothesis that a given design will be profitable, the cost of a Type I Error (false positive) is $300,000 and the cost of a Type II Error (false negative) is $200,000 of passing. If p is the probability that the hypothesis is true, the expected costs of both decision errors are equal if:
p×$300,000 = (1-p)×(200,000)
or
p×$300,000 = 200,000-p×200,000
or
p×($300,000+200,000) = 200,000
or
p = 200,000/($300,000+200,000) = 40%.
So long as he is more than 40% confident that the design will be successful, carrying the design will minimize expected decision error costs.
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. For a given quantity, a monopoly's marginal revenue is always greater than the price associated with that quantity. 2. When regulating a natural monopoly one should set the regulatory price such that the monopoly will produce the efficient level of output. 3. Deadweight loss because of a monopoly can be attributed to the fact that monopolies produce at a quantity where the price of the good exceeds the marginal cost of producing the last unit. 4. When there are significant differences among customers, a monopolist will look for opportunities to price discriminate. 5. Distributing goods equally among consumers would be not only fair but efficient.
Use the following supply and demand graph to answer the question below.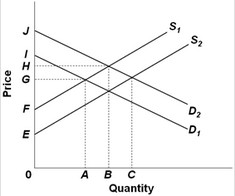 S1 and D1 represent the current market supply and demand, respectively. S2 and D2 represent the socially optimal supply and demand. The positions of the graphs indicate that there is (are) external
S1 and D1 represent the current market supply and demand, respectively. S2 and D2 represent the socially optimal supply and demand. The positions of the graphs indicate that there is (are) external
A. benefits from production and external costs from consumption of the product. B. costs from production and external benefits from consumption of the product. C. costs from production and consumption of the product. D. benefits from production and consumption of the product.
The goal of the manager of a firm is sales maximization. The firm will produce
a. the output level at which MR = 0. b. as much output as it can. c. the same output that it would if the goal was profit maximization. d. the same output that it would if the goal was cost minimization.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 9.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.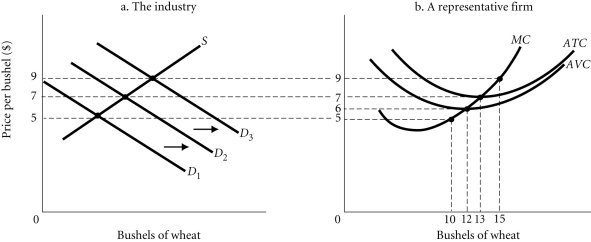 Figure 9.2Refer to Figure 9.2. The firm's ________ point is at a price of $6.
Figure 9.2Refer to Figure 9.2. The firm's ________ point is at a price of $6.
A. shut down B. profit maximizing C. break even D. loss maximizing