If aggregate demand shifts outward over a long period of time, with aggregate supply held constant, the economy should experience
A. unemployment.
B. recession.
C. budget surpluses.
D. inflation.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Which two pieces of legislation were passed in 1914?
a. Sherman Antitrust and Clayton Act b. Clayton Act and Robinson-Patman Act c. Robinson-Patman Act and Celler-Kefauver Act d. Clayton Act and Federal Trade Commission Act e. Sherman Antitrust Act and Federal Trade Commission Act.
Great Benefit is a health insurance company with two types of customers: healthy persons and sickly persons. A healthy person has 1-to-5 odds of getting ill, and a sickly person has 1-to-1 odds of getting ill. However, the insurance company cannot distinguish between healthy and sickly persons. Brett is a risk-averse person who purchases health insurance from Great Benefit. Without insurance, Brett's income will be $8,000 if he remains healthy and $2,000 if he becomes ill. Brett's situation is diagrammed below.
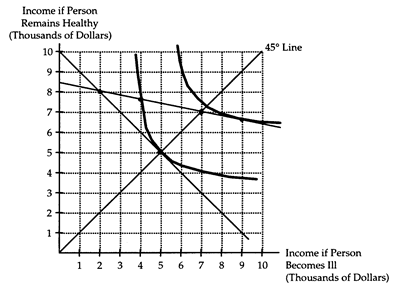
(i) Is Brett a healthy person or a sickly person? How can you tell?
(ii) Suppose Great Benefit offers two policies-one at fair odds for healthy persons and one at fair odds for sickly persons-that can be purchased in unlimited quantities. What type of policy and how much insurance will Brett choose to purchase?
(iii) What type of information problem does the insurance company face? What limit should the insurance company place on insurance at "healthy" odds to deal with this problem?
The price received by sellers in a market will decrease if the government
a. increases a binding price floor in that market. b. increases a binding price ceiling in that market. c. decreases a tax on the good sold in that market. d. None of the above is correct.
To maximize total profit in the short run, a perfectly competitive firm must find:
a. the quantity at which total revenue is at a maximum. b. the quantity at which total cost is at a minimum. c. the quantity at which total revenue is at a maximum and total cost is at a minimum. d. the quantity at which total revenue exceeds total cost by the greatest amount.