If in market equilibrium the true marginal cost of producing a good exceeds the marginal cost incurred by the firm,
a. not enough of the product is being produced.
b. the price charged for the good is too high.
c. the good produces a positive externality.
d. the good produces a negative externality.
e. the government should produce the good.
D
You might also like to view...
A difference between the classical and new classical models is that
a. classical economists assumed that labor suppliers knew the real wage, while the new classical economists assume they form a rational expectation of the real wage. b. classical economists assumed that the money wage was flexible while the new classical economists assume it was fixed. c. new classical models do not assume perfect competition. d. labor supply in the classical model is a function of the real wage while labor supply depends on the money wage in the new classical model. e. both a and c.
This graph depicts a tax being imposed, causing demand to shift from D1 to D2. According to the graph shown, the tax caused:
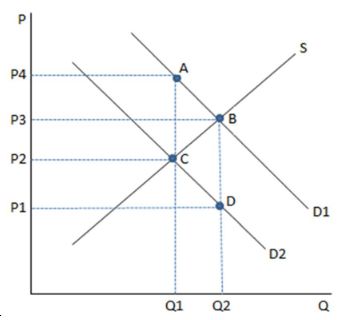
A. an increase in consumption from Q1 to Q2.
B. a decrease in consumption from Q2 to Q1.
C. a decrease in the price consumers pay from P3 to P1.
D. a decrease in the price the suppliers receive from P3 to P1.
A market is in equilibrium:
A. if the amount producers want to sell is equal to the amount consumers want to buy. B. whenever the demand curve is downsloping and the supply curve is upsloping. C. provided there is no surplus of the product. D. at all prices above that shown by the intersection of the supply and demand curves.
According to the capture hypothesis of regulation
A) regulation favors producers over consumers because the producers were able to pay off the regulators. B) regulation eventually favors producers over consumers because the producers have more at stake than individual consumers. C) regulation benefits the regulators and the legislators who support the regulation by enabling them to obtain favors from both producers and consumers. D) regulation benefits the consumers over producers because the number of consumers is greater than the number of producers, giving the consumers more political clout.