When profits are the result of pure luck, they can be distinguished from profits attributable to correct predictions by
A) asking the people who profited.
B) finding out whether the profits were earned through effort.
C) no known empirical criteria.
D) whether or not they were generally anticipated.
C
You might also like to view...
Refer to the Article Summary. The pricing method described in the article is referred to as first-degree price discrimination. First-degree price discrimination is also known as
A) perfect price discrimination. B) odd pricing. C) two-part tariff pricing. D) arbitrage.
Assume that in year 1 you pay an average tax rate of 20 percent on a taxable income of $20,000. In year 2, you pay an average tax rate of 25 percent on a taxable income of $30,000. Assuming no change in tax rates, the marginal tax rate on your additional
$10,000 of income is: A. 5 percent. B. 12 percent. C. 35 percent. D. 42 percent.
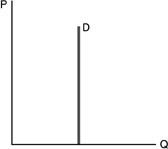 Refer to the above figure. Demand is
Refer to the above figure. Demand is
A. perfectly elastic. B. unitary elastic. C. perfectly inelastic. D. undetermined without more information.
Offshoring often results from:
A. diminished human capital of American workers. B. overly restrictive trade policies. C. a change in comparative advantage. D. a desire to help out workers in low-income economies.