An electronic package with a surface area of 1 m2 placed in an orbiting space station is exposed to space. The electronics in this package dissipate all 1 kW of its power to the space through its exposed surface. The exposed surface has an emissivity of 1.0 and an absorptivity of 0.25. Determine the steady-state exposed surface temperature of the electronic package (a) if the surface is exposed to a solar flux of 750?W/m2, and (b) if the surface is not exposed to the sun.
What will be an ideal response?
For an electronic package with given surface area, power dissipation, surface emissivity and absorptivity to solar radiation and the solar flux, the surface temperature with and without incident solar radiation is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 Steady operating conditions exist.
Analysis Apply conservation of energy (heat balance) to a control volume about the electronic package in rate form
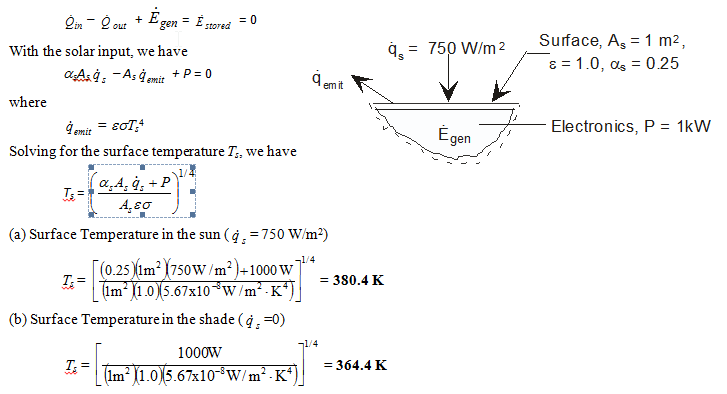
Discussion In orbit, the space station would be continuously cycling between shade and sunshine, and a steady-state condition would not exist.
You might also like to view...
Retempering of mortar, if needed, should be generally done within ______.
A) 1 h of the initial preparation of mortar. B) 4 h of the initial preparation of mortar. C) 5-1/2 h of the initial preparation of mortar. D) 2-1/2 h of the initial preparation of mortar. E) none of the above.
"Kosher" meat comes from animals with cloven hooves
Indicate whether this statement is true or false.
Cylinders become glazed where the piston rings contact the cylinder wall.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
What is the significance of the number 120 in the formula used to determine the frequency of the generated waveform?
What will be an ideal response?