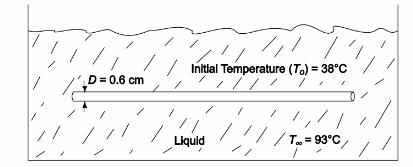
A 0.6-cm-diameter mild steel rod at 38°C is suddenly immersed in a liquid at 93°C with ch = 110 W/(m2 K). Determine the time required for the rod to warm to 88°C.
GIVEN
• A mild steel rod is suddenly immersed in a liquid
• Rod diameter (D) = 0.6 cm = 0.006 m
• Initial temperature of the rod (To) = 38°C
• Liquid temperature (T?) = 93°C
• Heat transfer coefficient ( ch ) = 113.5 W/(m2 K)
FIND
• The time required for the rod to warm to 88°C
ASSUMPTIONS
• The rod is 1% carbon steel
• Constant thermal conductivity
• End effects are negligible
• The rod is very long compared to its diameter
• There is radial conduction only in the rod
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
For 1% carbon steel at 20°C:
Thermal conductivity (k) = 43 W/(m K) Specific heat (c) = 473 J/(kg K) Density (?) = 7801 kg/m3 Thermal diffusivity (?) = 1.172 × 10–5 m2/s. [? = k/?c].
(a) The Biot number is calculated first to check if the internal resistance is negligible
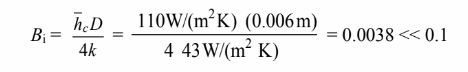
Therefore, the internal resistance of the rod is negligible.
The temperature-time history of the rod,
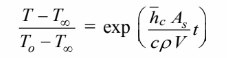
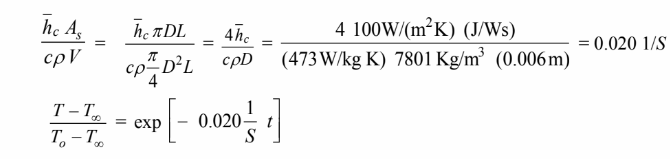
Solving for the time
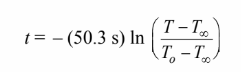
The time required to reach 88°C is
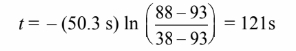
You might also like to view...
A stars exhibit strong hydrogen absorption lines because the surface temperature of 10,000 K is high enough to place most hydrogen in an excited, but not yet ionized, state
The transitions from this excited state then correspond to visible light wavelengths. Which of the following statements is a plausible explanation for why G stars exhibit weak hydrogen absorption lines? A) G stars contain very little hydrogen. B) At these high temperatures, nearly all the hydrogen is ionized, and unable to interact with light. C) G stars are too cool to excite hydrogen atoms to the first energy level from which they can then absorb visible wavelengths of light.
A certain source of sound waves radiates uniformly in all directions. At a distance of 20 m from the source the intensity level is 51 db. What is the total acoustic power output of the source, in watts?
(Note: The reference intensity I0 is 1.0 × 10-12 W/m2.)
In an isobaric process 4.0 × 10^4 J of work is done on a quantity of gas while its volume changes from 2.5 m3 to 1.5 m3 . What is the pressure during this process?
a. 3.4E+4 Pa b. 2.8E+4 Pa c. 4.0E+4 Pa d. 4.6E+4 Pa
Hydrogen lines are strongest in class A stars
Indicate whether the statement is true or false