In both monopolistic competition and perfect competition,
A) firms sell identical products.
B) there is easy entry and exit.
C) firms are price takers.
D) firms face horizontal demand curves.
E) the marginal revenue curve and the demand curve are the same.
B
You might also like to view...
Use the figure below to answer the following question.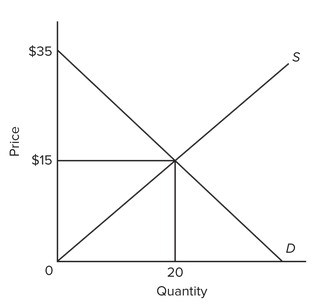 At equilibrium, economic surplus is
At equilibrium, economic surplus is
A. 200. B. 350. C. 150. D. 700.
If the demand curve for bottled water shifts rightward and the supply curve of bottled water shifts rightward, the equilibrium
A) price of bottled water definitely increases. B) price of bottled water definitely decreases. C) quantity of bottled water definitely increases. D) quantity of bottled water definitely decreases.
This table shows the total costs for various levels of output for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market.PriceQuantityTC$500$10.00$501$20.00$502$27.50$503$77.50$504$147.50$505$250.00According to the table shown, what is the firm's marginal cost from producing the 2nd unit?
A. $20.00 B. $10.00 C. $7.50 D. $27.50
Assume that foreign capital flows from a nation increase due to political uncertainly and increased risk. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the GDP Price Index and monetary base in the context of the Three-Sector-Model? a. The GDP Price Index rises and monetary base rises
b. The GDP Price Index rises and monetary base falls. c. The GDP Price Index and monetary base fall. d. The GDP Price Index and monetary base remain the same. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.