Why do we need new forms of technology to make it possible to journey to the nearest stars within a human lifetime?
What will be an ideal response?
Present rockets operate through chemical reactions, i.e., ordinary burning, which is a relatively inefficient process. To achieve high speeds requires lots of additional fuel, but the added weight of the fuel makes it more difficult to increase the rocket's speed. Such chemical rockets therefore have a fundamental limit to their speed and can go no faster than about 0.1 percent of the speed of light, which is not enough to reach the nearest stars (more than a light year away) in less than 1000 years.
You might also like to view...
The Higgs field is best described as a field that
If all the asteroids were gathered into a single object, it would make an object
A) about the size of Earth's moon. B) about the size of the Earth. C) about half the diameter of Earth's moon. D) with enough mass to gather hydrogen and helium and become a gas giant.
Due to inertia, perhaps a railroad train in motion should continue moving indefinitely when its engine is turned off. This is not observed because railroad trains
A) aren't massive enough. B) are too heavy. C) ride on straight tracks. D) encounter opposing forces.
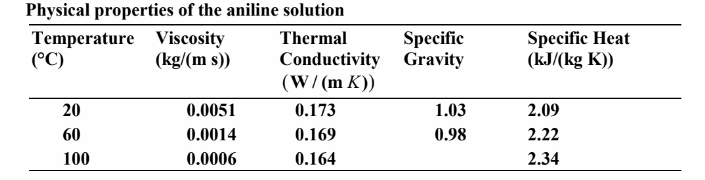
An aniline-alcohol solution is flowing at a velocity of 3 m/s through a long, 2.5 cm-ID thin-wall tube. Steam is condensing at atmospheric pressure, on the outer surface of the tube, and the tube-wall temperature is 100°C. The tube is clean, and there is no thermal resistance due to a scale deposit on the inner surface. Using the physical properties tabulated below, estimate the heat transfer coefficient between the fluid and the pipe using and compare the results. Assume that the bulk temperature of the aniline solution is 20°C and neglect entrance effects.
GIVEN
• An aniline-alcohol solution flowing through a thin-walled tube
• Tube is clean with no scaling on inner surface
• Velocity (V) =3 m/s
• Inside diameter of tube (D) = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
• Tube wall surface temperature (Ts) = 100°C
• Solution has the properties listed above
• Solution bulk temperature (Tb)= 20°C FIND
• The heat transfer coefficient ( ch ) using: (a) Equation (7.61) (b) Equation (7.66)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• Entrance effects are negligible
• Thermal resistance of the tube is negligible
• Tube wall temperature is constant and uniform
• Fully developed flow
SKETCH

PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
The density of water ? 1000 kg/m3