Suppose the exchange rate falls from $1.20 Canadian per U.S. dollar to $1.10 Canadian per U.S. dollar. U.S. exports will ________, U.S. imports will ________, and U.S. aggregate demand will ________
A) decrease; increase; decrease
B) decrease; increase; increase
C) increase; decrease; increase
D) increase; increase; increase
C
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph to answer the next question.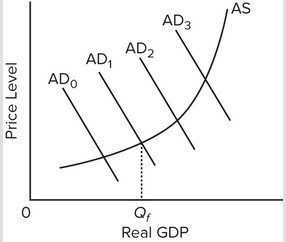 In the diagram, Qf is the full-employment output. An expansionary fiscal policy would be most appropriate and needed if the economy's present aggregate demand curve were at
In the diagram, Qf is the full-employment output. An expansionary fiscal policy would be most appropriate and needed if the economy's present aggregate demand curve were at
A. AD0. B. AD1. C. AD2. D. AD3.
One of the economic costs of holding currency is that
A) it fulfills no transactions role. B) it fulfills no precautionary role. C) its real value always increases. D) it earns no interest income.
What are diseconomies of scale and why might they occur?
What will be an ideal response?
The 45-degree line used in a consumption function represents:
a. the saving function. b. all points at which saving equals disposable income. c. all points at which consumption equals saving. d. all points at which all disposable income is consumed. e. the aggregate income of the economy.