Is discount lending used to keep banks from failing? Explain.
What will be an ideal response?
Not really. Discount loans to banks made by Fed require the bank post adequate collateral. If a bank has adequate collateral and is in good shape under most circumstances it should be able to borrow from another bank at the federal funds rate that, since 2002, is below the discount rate. If a bank has to come to the Fed for a loan it is a bank that cannot get a loan from another bank and if they can't provide collateral they are a bank that is likely to fail and probably should fail. The Fed may try to merge the bank into another bank, however, discount lending is not used to keep insolvent banks afloat.
You might also like to view...
The economy pictured in the figure below has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 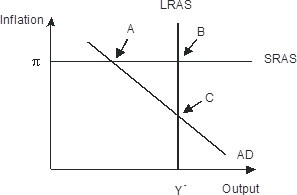
A. recessionary; B B. recessionary; C C. recessionary; A D. expansionary; A
If a product is narrowly defined, it is likely to
A) have many substitutes and therefore its demand is elastic. B) have few substitutes, and therefore its demand is less elastic. C) be unique, and therefore its demand is inelastic. D) be unique and have many substitutes. E) have a larger proportion of income spent on it.
Explain how each of the following events would affect the short-run aggregate supply curve
a. A decrease in the price level b. A decrease in what the price level is expected to be in the future c. A price level that is currently lower than expected d. An unexpected decrease in the price of an important raw material e. A decrease in the labor force
Suppose new research shows that soy milk and other products derived from soybeans provide more health benefits than previously thought. At the same time, drought conditions result in extensive damage to the soybean crop
What will be the combined impact of these two factors on the equilibrium price and quantity of soybeans? A) Price will decrease, but the effect on quantity is indeterminate. B) Price will increase, but the effect on quantity is indeterminate. C) Quantity will decrease, but the effect on price is indeterminate. D) Quantity will increase, but the effect on price is indeterminate.