The classical dichotomy argues that changes in the money supply
a. affect both nominal and real variables.
b. affect neither nominal nor real variables.
c. affect nominal variables, but not real variables.
d. do not affect nominal variables, but do affect real variables.
c
You might also like to view...
The payoff matrix below shows the payoffs (in millions of dollars) for two firms, A and B, for two different strategies, investing in new capital or not investing in new capital. 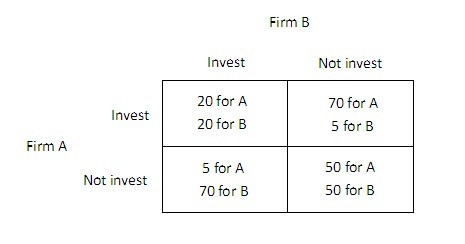 An industry spy from firm A comes to firm B and offers to pay B in exchange for B's certain and enforceable promise to not invest. What is the most that firm A will be willing to pay B to not invest?
An industry spy from firm A comes to firm B and offers to pay B in exchange for B's certain and enforceable promise to not invest. What is the most that firm A will be willing to pay B to not invest?
A. $30 million. B. $50 million. C. $20 million. D. $35 million.
A firm manager predicts and reacts to the moves of the firm’s competitors within the industry. What concept is illustrated by this example?
a. perfect competition b. prisoners’ dilemma c. economies of scale d. mutual interdependence
An equilibrium in the labor market is a situation in which:
A. there is no pressure for wages to change. B. there is no unemployment. C. wages exceed minimum wage. D. marginal revenue product equals the wage.
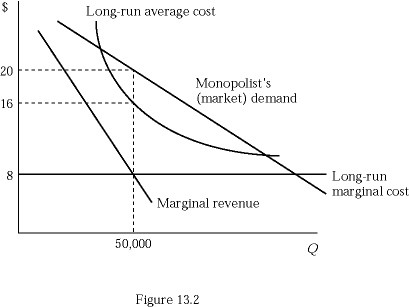 Consider an unregulated monopoly in Figure 13.2. The firm's profit at the profit maximizing output level is:
Consider an unregulated monopoly in Figure 13.2. The firm's profit at the profit maximizing output level is:
A. $600,000. B. $400,000. C. $200,000 D. $0.