What is the utility of studying weather on Mars or Venus, our planetary companions? Explain
What will be an ideal response?
Mars and Venus, in addition to being conveniently nearby, are very similar to
Earth is size and the existence of an atmosphere (denser on Venus, much less dense on
Mars). The similarities mean that these planets can be used to test the same physics and
physical models used on Earth (with changes appropriate to conditions on the respective
planet) to see whether they can make predictions for all three planets.
You might also like to view...
Earth sends out more signals into space by accident than with intent
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Explain how the essential features of special relativity imply that a beam of light from a fast moving spaceship will always be observed to moving at the speed of light
What will be an ideal response?
How do scientists estimate how old the universe is?
A) They look up the answer in a book. B) They measure how fast the Sun is losing energy, and how much energy it has to lose. C) They measure the abundances of radioactive elements in meteorites, and use their half-lives to calculate the age. D) They measure the speeds and distances of galaxies, and calculate the time it took for them to travel that distance. E) They make a guess; no one really knows how old the universe is.
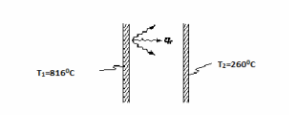
Two large parallel plates with surface conditions approximating those of a blackbody are maintained at 816 and 260°C, respectively. Determine the rate of heat transfer by radiation between the plates in W/m2 and the radiative heat transfer coefficient in W/(m2 K).
GIVEN
• Two large parallel plates, approximately black bodies
• Temperatures
? T1 = 816°C = 1089 K
? T2 = 260°C= 533 K FIND
(a) Rate of radiative heat transfer (qr/A) in W/m2 (b) Radiative heat transfer coefficient (hr) in W/(m2 K) ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state prevails
• Edge effects are negligible
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Stefan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 ? 10–8 W/(m2 K)