According to Keynesian economics, if there are unutilized resources in the economy and aggregate demand decreases
A) real GDP will rise and price level will remain constant.
B) real GDP will fall and price level will remain constant.
C) real GDP will rise and price level will rise.
D) real GDP will rise and price level will fall.
B
You might also like to view...
Consider a lake stocked with fish. The total value of fish caught at the lake depends on the number of fishers, as shown in the accompanying table. As the table indicates, 1 fisher can catch $36 worth of fish in a day, 2 fishers can catch a total of $66 worth of fish, 3 fishers can catch a total of $90 worth of fish, and so forth. The fishers are identical, and the opportunity cost of a day at the lake is $18 for each fisher.
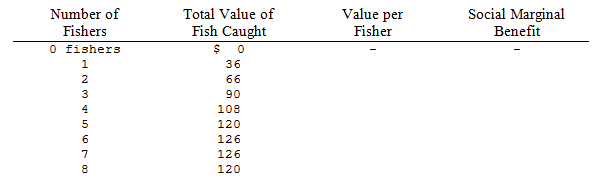
(i) Complete the table by calculating the value of each fisher's catch, on average, and the social marginal benefit of the lake.
(ii) If use of the lake is nonexcludable, how many fishers come to the lake? What is the total value of their catch? What is their total cost? What is the social gain from the existence of the lake?
(iii) What is the optimal number of fishers at the lake? What is the social gain if this optimum is achieved?
(iv) What entrance fee would lead to the optimal outcome?
At an interest rate of 5 percent, the present value of $1,000 to be received two years from today is
A) less than $875. B) between $875 and $925. C) between $925 and $975. D) more than $975.
If a country had a nominal GDP of $7,664 billion and a real GDP of $9,346 billion, what was the GDP deflator?
a. 80 b. 82 c. 120 d. 122
What are the policies usually advocated by supply side economists? How do they justify these proposals?