In Figure 2.1, a "D" for Demand would go in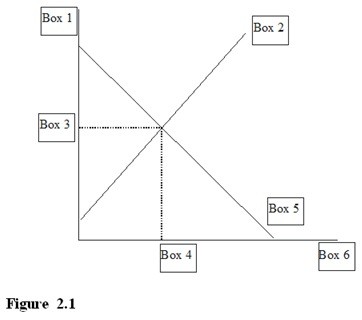
A. Box 4.
B. Box 5.
C. Box 6.
D. Box 2.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
During a recession, spending on ________ tends to fall more dramatically than spending on ________
A) nondurable goods; durable goods B) durable goods; nondurable goods C) food; cars D) necessities; luxuries
Because of an expected rise in interest rates in the future, a banker will likely
A) make long-term rather than short-term loans. B) buy short-term rather than long-term bonds. C) buy long-term rather than short-term bonds. D) make either short or long-term loans; expectations of future interest rates are irrelevant.
A risk-averse individual prefers
A) the utility of expected income of a risky gamble to the expected utility of income of the same risky gamble. B) the expected utility of income of a risky gamble to the utility of expected income of the same risky gamble. C) outcomes with 50-50 odds to those with more divergent probabilities, no matter what the dollar outcomes. D) outcomes with higher probabilities assigned to more favorable outcomes, no matter what the outcomes are. E) outcomes with highly divergent probabilities so that one of the outcomes is almost certain.
Suppose tax laws were reformed to encourage saving by increasing the rate of return on savings. Which of the following would be true?
a. Both the income effect and the substitution effect would tend to increase the amount of money a household saved. b. The income effect would tend to increase household savings while the substitution effect would tend to decrease household savings. c. The income effect would tend to decrease household savings while the substitution effect would tend to increase household savings. d. Both the income effect and the substitution effect would tend to decrease the amount of money a household saved.