In chapter 1 your authors marveled at the way highway traffic is orderly and self-regulating. In chapter 6, however, they discuss a growing problem on urban roadways—congestion. What's the cause of roadway congestion?
A) Typically, road use is a scarce good with a zero price tag.
B) Not enough drivers have studied economics.
C) More and more drivers think only of themselves.
D) Population growth
A
You might also like to view...
An automobile manufacturer imported equipment in order to produce a particular model at low cost. Falling demand, however, forced it to cease producing that model, and the company took a large loss because the equipment was not usable for producing other models. The equipment was characterized by:
a. locational specificity. b. dedicated specificity. c. human specificity. d. task specificity.
If two goods are complementary goods, then
A. The cross-price elasticity sign is not important. B. The cross-price elasticity sign will be negative. C. The cross-price elasticity will be greater than 1. D. The cross-price elasticity sign will be positive.
Use the figure below to answer the following question.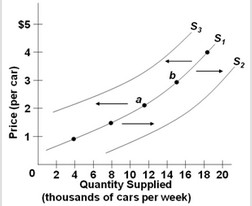 The diagram shows three supply curves for cars today. Which of the following would cause the supply of cars to shift from S1 to S2?
The diagram shows three supply curves for cars today. Which of the following would cause the supply of cars to shift from S1 to S2?
A. an increase in the price of cars in the market B. a decrease in the number of car producers C. expectations of higher car prices in the future D. expectations of lower car prices in the future
Competition means that:
A. sellers can manipulate market price by causing product scarcities. B. there are independently acting buyers and sellers in each market. C. a product can be purchased at a number of different prices. D. there is more than one seller in a market.