The total multiplier of government expenditure is
A) zero.
B) between zero and one.
C) one.
D) larger than one.
B
You might also like to view...
With discretionary policy making, fiscal and monetary policies are usually
A) immune to any lag times that might counter their effectiveness. B) immune to any political overtones. C) set according to pre-established standards that do not take into account any changes in the economy. D) undertaken in response to or anticipation of some change in the overall economy.
Assume a fixed demand for money curve and the Fed increases the money supply. In response, people will:
a. sell bonds, thus driving up the interest rate. b. sell bonds, thus driving down the interest rate. c. buy bonds, thus driving up the interest rate. d. buy bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
During the contraction phase of the business cycle,
a. prices fall relative to costs, reducing profit margins. b. costs fall relative to prices, reducing profit margins. c. prices fall relative to costs, increasing profit margins. d. costs fall relative to prices, increasing profit margins.
If the money supply in the economy were at MS2, to engage in contractionary policy the Federal Reserve Bank would use open market operation to move money supply to:
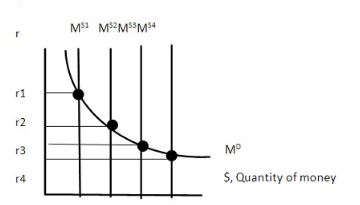
A. MS1
B. MS3
C. MS4
D. it would stay at MS2