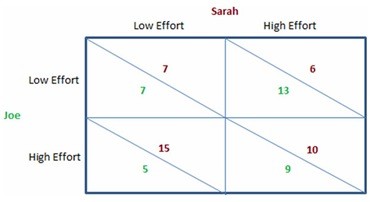
 This figure shows the payoffs involved when Sarah and Joe work on a school project together for a single grade. They both will enjoy a higher grade when more effort is put into the project, but they also get pleasure from goofing off and not working on the project. The payoffs can be thought of as the utility each would get from the effort they individually put forth and the grade they jointly receive.According to the figure shown, if Joe puts forth high effort, then Sarah should:
This figure shows the payoffs involved when Sarah and Joe work on a school project together for a single grade. They both will enjoy a higher grade when more effort is put into the project, but they also get pleasure from goofing off and not working on the project. The payoffs can be thought of as the utility each would get from the effort they individually put forth and the grade they jointly receive.According to the figure shown, if Joe puts forth high effort, then Sarah should:
A. give an ultimatum.
B. put forth high effort.
C. put forth low effort.
D. leave school.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below.________ inflation will eventually move the economy pictured in the diagram from short-run equilibrium at point ________ to long-run equilibrium at point ________, 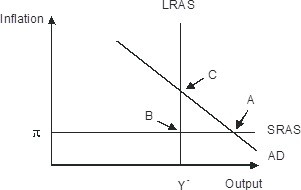
A. Rising; B; C B. Falling; A; C C. Falling; A; B D. Rising; A; C
Suppose the U.S. can produce 10 units of food and five units of clothing (or any such linear combination) and Canada can produce six units of food and four units of clothing (or any such linear combination)
If trade occurs between these two countries, which should produce more food and which more clothing?
The Coase theorem asserts that private economic actors can solve the problem of externalities among themselves, without government intervention, regardless of whether those actors incur significant costs in reaching and enforcing an agreement
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the information given. In the long run, a fall in the price level from 100 to 75 will:
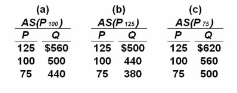
Suppose the full employment level of real output (Q) for a hypothetical economy is $500, the
price level (P) initially is 100, and prices and wages are flexible both upward and downward.
Use the following short-run aggregate supply schedules to answer the question.
A. decrease real output from $500 to $440.
B. increase real output from $500 to $620.
C. change the aggregate supply schedule from (a) to (c) and produce an equilibrium level of
real output of $500.
D. change the aggregate supply schedule from (a) to (b) and produce an equilibrium level of
real output of $500.