Periodic fluctuations in GDP are called business cycles
a. True
b. False
A
You might also like to view...
Consider the utility function 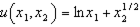
c. The marginal utility of a good is defined as the change in utility from additional consumption of that good (holding all else constant). Derive the marginal utility of 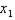
d. Why does an ordinal approach to utility theory not any attention to what you derived in (c)?
e. Why does an ordinal approach to utility not treat the marginal rate of substitution the way it treats the marginal utility concept?
What will be an ideal response?
Explain why debt is usually measured using the debt-to-GDP ratio rather than the absolute amount of debt
What will be an ideal response?
Given the annual rate of inflation, the "rule of 70" allows one to:
A. determine whether the inflation is demand-pull or cost-push. B. calculate the accompanying rate of unemployment. C. determine when the value of a real asset will approach zero. D. calculate the number of years required for the price level to double.
A country has a trade deficit when
A. government spending is greater than tax receipts. B. its exports are less than its imports. C. its exports equal its imports. D. its exports exceed its imports.