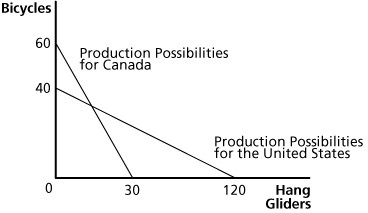
 Figure 18.1Refer to Figure 18.1. The opportunity cost of bicycles in Canada is:
Figure 18.1Refer to Figure 18.1. The opportunity cost of bicycles in Canada is:
A. 1/2 of a hang glider.
B. 2/3 of a hang glider.
C. 2 hang gliders.
D. 4 hang gliders.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
For most of World War II, the United States economy temporarily operated ____________ the production possibilities frontier.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Using aggregate demand and aggregate supply, explain what happens in the short run if the Federal Reserve raises interest rates in the economy. Be sure to detail what happens to aggregate demand, the price level, the level of GDP, and unemployment
Assume that the economy is at full employment before the interest rate increase.
According to economists who explain the Phillips curve, a decline in the unemployment rate causes higher rates of inflation because
a. workers are concerned about protecting their jobs and so they accept smaller wage increases b. during periods of GDP growth, firms find it easier to pay higher wage rates and charge higher prices without worrying about losing markets c. firms decrease production and compete less aggressively for workers during periods of inflation d. workers feel less secure about their jobs and demand higher pay raises e. the Laffer curve comes into effect
Suppose that at the prevailing yen-dollar exchange rate there is an excess demand for dollars. To stabilize exchange rates, the United States might
A. Lower taxes. B. Raise interest rates. C. Pursue contractionary monetary policy. D. Reduce government spending.