If a nation is initially producing at a point on its production possibilities frontier, then it can increase its production of one good only by
A. decreasing the price of the other good.
B. increasing the production of the other good.
C. holding constant the production of the other good.
D. decreasing the production of the other good.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is most likely to lead to an increase in the rental price of apartments near your campus?
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the graph shown. Initially, the market is in equilibrium with price equal to $25 and quantity equal to 100. As a result of a per-unit tax imposed by the government, the supply curve shifts from S0 to S1. The effect of the tax is to: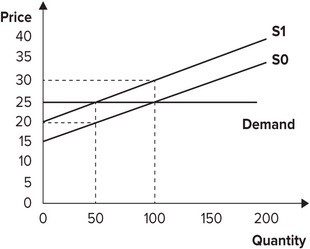
A. reduce producer surplus by $400. B. give government tax revenues of $400. C. reduce producer surplus by $375. D. give government tax revenues of $100.
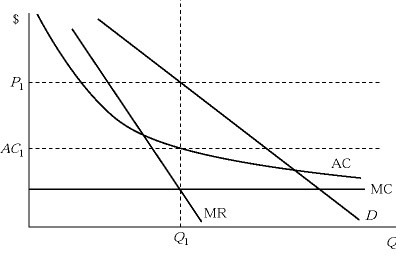
 Figure 8.1 depicts demand and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. At the profit-maximizing output level:
Figure 8.1 depicts demand and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. At the profit-maximizing output level:
A. this firm is earning economic profits equal to zero. B. this firm is earning economic profits equal to Q1(P1 - AC1). C. this firm is earning economic profits equal to P1(Q1 - AC1). D. this firm is in long-run equilibrium.
To be counted as unemployed in the United States a person has to be
A. at least 16 and less than 65 and actively seeking employment. B. at least 16, out of work, and actively seeking employment. C. out of work and actively seeking employment. D. at least 21 and out of work.