Monopolization of both the labor market and the output market results in
A) higher wages than when both are competitive.
B) a higher output price than when both are competitive.
C) a lower level of output than when both are competitive.
D) All of the above.
D
You might also like to view...
In perfect competition, all the following situations arise except ________
A. firms produce an identical good or service B. each firm chooses the price at which to sell the good it produces C. firms can sell any quantity they choose to produce at the market price D. buyers know each seller's price
A demand curve is described as perfectly inelastic if
A. the same quantity is purchased regardless of price. B. the same price is charged regardless of quantity sold. C. neither price nor quantity demanded ever change. D. only quantity demanded can change.
If the graph shown represents Stella's budget constraint, and she has income of $48 to spend on these two items, Stella could choose which consumption bundle?
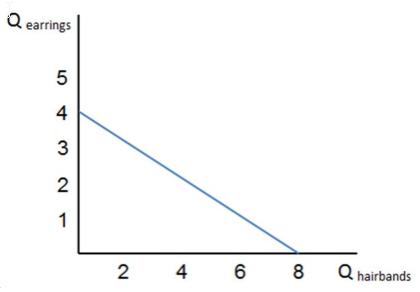
A. One pair of earrings and seven hairbands
B. Four pairs of earrings and eight hairbands
C. Three pairs of earrings and six hairbands
D. Two pairs of earrings and four hairbands
Moral hazard and adverse selection are both examples of
a. the principal-agent problem. b. externalities in consumption. c. efficiency in markets. d. perfect information. e. asymmetric information.