An airplane moves 140 m/s as it travels around a vertical circular loop which has a 1.0-km radius. What is the magnitude of the resultant force on the 70-kg pilot of this plane at the bottom of this loop?
a. 2.1 kN
b. 1.4 kN
c. 0.69 kN
d. 1.5 kN
e. 1.3 kN
B
You might also like to view...
Projectile Motion: A projectile is fired at an angle above the horizontal at a location where g = 9.8 m/s2. The initial x and y components of its velocity are 86.6 m/s and 50 m/s respectively. At what angle was the projectile fired above the horizontal?
A. 45° B. 60° C. 30° D. 90° E. 75°
State Kepler's three laws of planetary motion
What will be an ideal response?
Consider the problem described in Example 8.5. Show that the transient heating of the water in the pan, assuming the water to be well-mixed and thermally homogenous at any instant in time, can be expressed by the following:
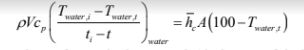
where V is the volume of water in the pan and A is the area of the bottom surface of the
pan. Solve this equation (numerically or otherwise) to determine the time required to
heat the water to (a) 50°C and (b) 80°C. Also, determine the total heat transfer to the
water in the pan in each case.
GIVEN
? A covered pan kept in stove-top burner
? Depth of pan (L)= 8 cm
? Pan bottom surface temperature (Ts) = 100°C
? Initial water temperature at top (T?) = 20°C
? Diameter of the pan (D) = 15 cm
FIND
? Show the expression for heat flow through convection to pan
? Time required and total heat transfer to water while heating the water to 500C and 800C
ASSUMPTIONS
? Radiation heat transfer is negligible
SKETCH
Refer to Example 8.5
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
From Appendix 2, Table 28, for dry air at the mean temperature of 60°C
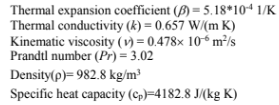
The color of a star is a measure of its
A) surface temperature B) chemical composition C) mass D) size