In the long run, if the demand curve of a monopolistically competitive firm is tangent to its average total cost curve then
A) the firm would earn an economic profit.
B) the firm would earn enough revenue to cover its variable costs, but not its fixed costs.
C) the firm would break even.
D) the firm would shut down temporarily.
C
You might also like to view...
The output losses from an adverse inflation shock are ________ and the output losses from a fall in potential output are ________.
A. large; small B. small; large C. permanent; temporary D. temporary; permanent
The level of real GDP in the long run is
A) potential GDP. B) determined solely by aggregate demand. C) affected by changes in the price level. D) the same as the level of nominal GDP in the long run.
What are economies of scale and diseconomies of scale? How do they arise? What do they imply for the shape of the LRAC curve?
What will be an ideal response?
The game in the figure is shown using a:
This figure displays the choices being made by two coffee shops: Starbucks and Dunkin Donuts. Both companies are trying to decide whether or not to expand in an area. The area can handle only one of them expanding, and whoever expands will cause the other to lose some business. If they both expand, the market will be saturated, and neither company will do well. The payoffs are the additional profits (or losses) they will earn.
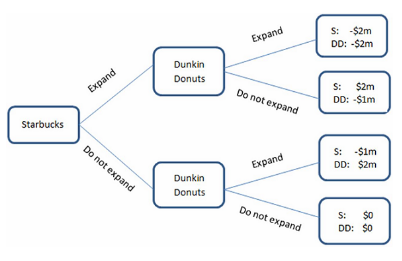
A. decision tree.
B. decision matrix.
C. flowchart.
D. graph.