In a(n) _________test, the part is subject to a specified stress, and if the part does not fail, the maximum possible crack length is then calculated.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
proof
You might also like to view...
Solve the set of difference equations derived in Problem 4.52 given the following values of the problem parameters
k = 40.0 W/(mK), disk thermal conductivity a = 1 ? 10–5 m2/s, disk thermal diffusivity Rs = 25 mm, disk radius Zs = 5 mm, disk thickness q" max = 3 x 106 W/m2, peak absorbed flux Ro = 50 mm, parameter in flux distribution Tinit = 20°C, disk initial temperature Determine the temperature distribution in the disk when the maximum temperature is 300°C. GIVEN - Difference equations developed in Problem 4.52 given the following values of the problem parameters FIND (a) Disk temperature distribution when the maximum temperature is 300°C
A rod with a positive charge is brought near a positively charged pith ball. The pith ball is suspended from an insulating string. The pith ball
A. will be attracted by the rod B. will be repelled by the rod C. will not be affected by the rod
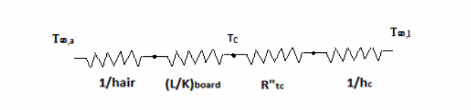
A thin, flat plate integrated circuit of 5 mm thickness is cooled on its upper surface by a dielectric liquid. The heat dissipation rate from the chip is 20,000 W/m2 and with the coolant flow at a free stream temperature of T?,l =250C, the convective heat transfer coefficient between the chip surface and the liquid is 1000 W/(m2 K). On the lower surface, the chip is attached to a circuit board, where the thermal contact resistance between the chip and the board is 10-4 m2.K/W. The thermal conductivity of board material is 1.0 W/m. K, and its other surface ( away from the chip) is exposed to ambient air at T?,a =200C where it is cooled by natural convection with the heat transfer coefficient of 30 W/(m2 K). (a) Determine the chip surface temperature under steady state condition for the
described conditions. (b) If the maximum chip temperature is not to exceed 750C, determine maximum allowable heat flux hat is generated by the chip. (c) A colleague suggests that in order to improve the cooling, you use a high conductivity bonding base at chip-board interface that would reduce the thermal contact resistance at the interface to 10-5 m2.K/W. Determine the consequent increase in the chip heat flux that can be sustained.
GIVEN

FIND
(a) Chip surface temperature under steady state condition
(b) Maximum allowable heat flux generated by the chip
(c) Consequent increase in chip heat flux if high conductivity bonding is used.
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state conditions prevail
The thermal conductivity of the wall (k) is constant
One dimensional conduction
Negligible radiation and thermal resistance between chip surface and the liquid.
SKETCH
The thermal circuit of problem is given by
An automobile travels due north with a constant speed of 81 km/h. All forces considered, the unbalanced force acting on the auto is
a. zero. b. southward. c. northward. d. downward. e. upward.