The CMS Co. began operations in January 2016. Listed below are selected transactions for 2016 and 2017:
?During 2016, $125,000 in R&D expenditures were made to develop a new product that was patented on July 1, 2016. CMS believes the patent will provide benefits for ten years. Legal fees incurred were $24,000.?On September 1, 2016, CMS paid EZ Company $180,000 for its patent on a successful product. The patent has six remaining years in its legal life.?On October 1, 2016,CMS applied for and received a trade name from the government. The legal costs associated with filing for the trade name were $10,000. In addition, during November 2016, the company incurred $50,000 in advertising its name. Benefits are expected indefinitely.?In early January 2017, CMS paid $20,000 in legal fees to defend the patent acquired from EZ. CMS's attorneys were successful in the lawsuit.?During 2017, R&D expenditures of $90,000 were incurred in the development of a product. A patent was received on December 1, 2017. Legal fees paid in connection with the patent were $15,000. The economic life of the product is expected to be five years.?
Required:
a.Prepare a partial balance sheet for CMS Company as of December 31, 2017, showing the intangible assets. In support of your answer, prepare a separate schedule for each intangible asset. The company amortizes its intangible assets using the straight-line method and recognizes amortization to the nearest month.b.Prepare a schedule to calculate CMS's expenses related to the above transactions for both 2016 and 2017.
What will be an ideal response?
?
| a. | CMS CompanyPartial Balance SheetDecember 31, 2017 | |||
| Intangible assets: | ? | |||
| ? | Patents (see Schedules 1, 2, and 3) | $187,150 | ||
| ? | Trade name (see Schedule 4) | 10,000 | ||
| ? | ? | Total intangible assets | $197,150 | |
| ? | ? | |||
| Patent-Schedule 1 | ? | |||
| ? | Cost | $24,000 | ||
| ? | Less: | 2016 amortization ($24,000´1/10´6/12) | (1,200) | |
| ? | ? | 2017 amortization | (2,400) | |
| ? | Book value of patent, 12/31/15 | $20,400 | ||
| ? | ? | |||
| Patent-Schedule 2 | ? | |||
| ? | Costs | $180,000 | ||
| ? | Less: 2016 amortization ($180,000´1/6´4/12) | (10,000) | ||
| ? | Add: Legal fees, 2017 | 20,000 | ||
| ? | Less: 2017 amortization ($190,000´1/5) | (38,000) | ||
| ? | Book value of patent, 12/31/15 | $152,000 | ||
| ? | ? | |||
| Patent-Schedule 3 | ? | |||
| ? | Costs | $15,000 | ||
| ? | Less: 2017 amortization ($15,000´1/5´1/12) | (250) | ||
| ? | Book value of patent, 12/31/15 | $14,750 | ||
| ? | ? | |||
| Trade name-Schedule 4 | ? | |||
| ? | Costs | $10,000 | ||
| ? | Book value of trade name, 12/31/15 | $10,000 | ||
| b. | ? | 2016 Expenses |
| ? | R&D expense | $125,000 |
| ? | Amortization expense-Patents ($1,200 + $10,000) | 11,200 |
| ? | Advertising expense | 50,000 |
| ? | Total expenses | $186,200 |
| ? | ? | ? |
| ? | 2017 Expenses | ? |
| ? | R&D expense | $ 90,000 |
| ? | Amortization expense-Patents ($2,400 + $38,000 + $250) | 40,650 |
| ? | Total expenses | $130,650 |
You might also like to view...
Sweet Dreams Corp. has prepared the following financial statements:

a) Set up a worksheet similar to the one in Exhibit 4-4, page 124, and calculate all of the ratios for Sweet Dreams Corp.
b) Verify the change in 2017 Sweet Dreams Corp’s ROE using the Du Pont method.
c) Using the Altman’s model for privately held firms and public ones, calculate the Z-score for Sweet Dreams Corp. Assume that the market value of Sweet Dreams Corp. is $1,200,000.
d) Calculate Sweet Dreams Corp.’s economic profit for these years and compare it to net income. Assume that the weighted average cost of capital is 12%.
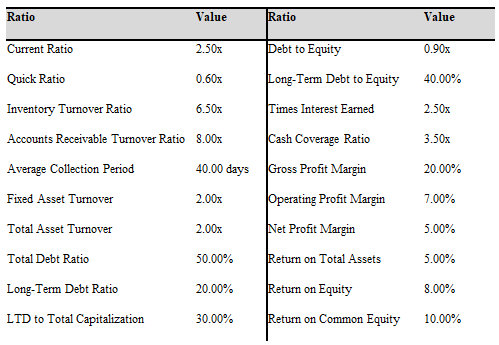
e) Using the following 2017 industry averages, evaluate Sweet Dreams Corp.’s financial situation. Set up a ratio analysis system similar to the one in Exhibit 3-6, page 92.
In the hypothetical Volkswagen engineer scenario, which is the lowest level ethical theory that suggests the engineer should not assist in the cheating scheme?
a. social group relativism b. cultural relativism c. virtue ethics d. deontology
Which of the following is a media measure?
A) consumer price index B) GDP per capita C) wholesale price index D) click-through rate E) human development index
Which types of consumers are least likely to respond to a direct marketer?
a. new contacts and nonrespondents b. nonregulars and new contacts c. nonregulars and nonrespondents d. nonregulars and new trails