What causes a substantial percentage of foodborne illnesses?
A) Pathogens
B) Unsanitary conditions
C) Poisonous dyes
D) Poisonous preservatives
Answer: A
Explanation: A) Correct. A substantial percentage of foodborne illnesses are caused by pathogens.
B) Incorrect. A substantial percentage of foodborne illnesses are caused by pathogens.
C) Incorrect. A substantial percentage of foodborne illnesses are caused by pathogens.
D) Incorrect. A substantial percentage of foodborne illnesses are caused by pathogens.
You might also like to view...
(2a2b)3 = ____
A. 4a3b3 B. 8a6b3 C. 8a6b6 D. 4a6b6
Which of the statements A–D is false?
A. Internal energy is a state function, while heat and work are not state functions. B. If we write “?H = MCP?T”, we are assuming that the heat capacity is constant. C. If we write “dH = MCPdT”, we are assuming either that the pressure of the system is constant or that enthalpy is independent of pressure. D. When Q or W is positive, this means that either heat is added to the system (Q> 0 ) or work is done on the system (W> 0), according to the sign convention in this book. E. None of these are false.
What is the kilowatt rating of an electric furnace rated at 240 V and 30 A?
A) 240 V × 30 A = 7,200 W, which is 72 kW B) 240 V/30 A = 8 kW C) 240 V × 30 A = 7,200 W, which is 7.2 kW D) Kilowatts cannot be calculated using only volts and amps.
Refer to Figure P2.27 and assume that vS = 15 V and RS = 100 ?. For iT = 0, 10, 20, 30, 80, and 100 mA:
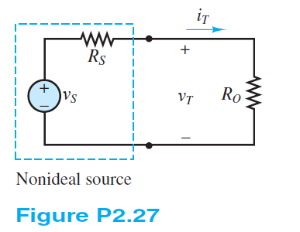
a. Find the total power supplied by the ideal source.
b. Find the power dissipated within the non-ideal source.
c. How much power is supplied to the load resistor?
d. Plot the terminal voltage vT and power supplied to the load resistor as a function of terminal current iT .